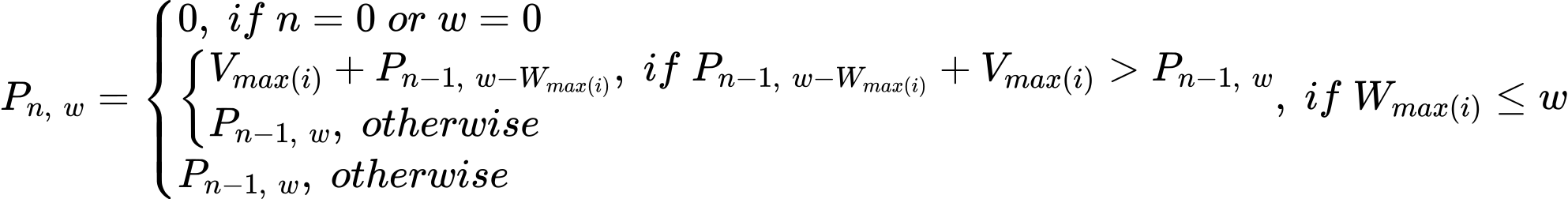문제
풀이
1. 알고 있어야 할 점
- 다이나믹 프로그래밍을 이용한다.
- 동적 계획법(動的計劃法, dynamic programming)이란 복잡한 문제를 간단한 여러 개의 문제로 나누어 푸는 방법을 말한다.[동적 계획법]
- 수식 $\newline n:\;담을\,수\,있는\,물건의\,수(담을\,수\,있는\,물건의\,번호:\,0 \leq i \leq n-1)$
$w:\;버틸\,수\,있는\,무게$
$i:\;물건의\,번호$
$max(i): 담을\,수\,있는\,물건의\,번호\,중\,최댓값(max(i) = n-1)$
$P_{n,\;w}:\;n개의\,물건을\,담을\,수\,있고,\,버틸\,수\,있는\,무게가\,w인\,배낭에\,넣을\,수\,있는\,물건들의\,가치합의\,최댓값$
$V_i:\;i\,물건이\,가치$
$W_i:\;i\,물건의\,무게$
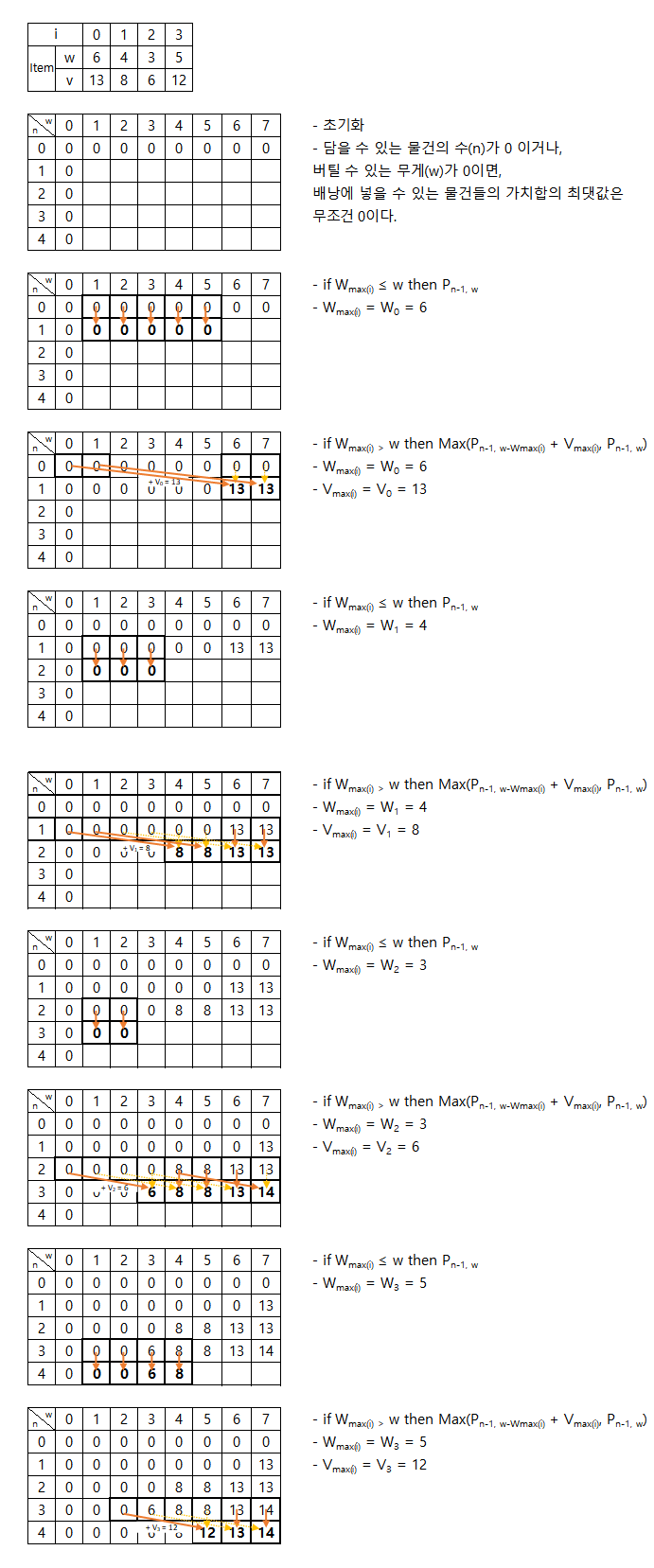
- 문제의 예제 1의 연산 과정
2. Step by Step
재귀를 사용하는 방법(timeout 발생)
1. 입력을 받는다.
- code ```kotlin val (numOfItems, maxWeight) = readln().split(“ “).map { it.toInt() } val items = Array(numOfItems) { readln().split(“ “).let { Item(it.first().toInt(), it.last().toInt()) } }
data class Item(val w: Int, val v: Int)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#### 2. 수식을 재귀 함수로 작성한다.
- code
```kotlin
fun p(n: Int, w: Int, items: Array<Item>): Int = when {
n == 0 || w == 0 -> 0
items[n-1].w <= w -> kotlin.math.max(p(n-1, w-items[n-1].w, items) + items[n-1].v, p(n-1, w, items))
else -> p(n-1, w, items)
}
|
3. 결과 값을 출력한다.
- code
1
| println(p(numOfItems, maxWeight, items))
|
반복문을 사용하는 방법
1. 입력을 받는다.
- code ```kotlin val (numOfItems, maxWeight) = readln().split(“ “).map { it.toInt() } val items = Array(numOfItems) { readln().split(“ “).let { Item(it.first().toInt(), it.last().toInt()) } }
data class Item(val w: Int, val v: Int)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
### 2. 가치합의 최댓값 저장할 변수를 선언한다.
- 정수형 2차원 배열을 이용한다.
- 배열의 각 값은 0으로 초기화 한다.
- code
```kotlin
val p = Array(numOfItems + 1) { IntArray(maxWeight + 1) { 0 } }
|
2. 수식을 반복문으로 작성한다.
- 배열을 0으로 초기화 하였기 때문에 n=0, w=0인 경우에 대해서는 이미 0이 입력되어 있다.
- 그러므로, 1부터 반복문을 시작한다.
- code
1
2
3
4
5
6
| for(n in (1..numOfItems)) {
for(w in (1..maxWeight)) {
val item = items[n-1]
p[n][w] = if(w >= item.w) kotlin.math.max(p[n-1][w-item.w] + item.v, p[n-1][w]) else p[n-1][w]
}
}
|
3. 결과 값을 출력한다.
- code
1
| println(p(numOfItems, maxWeight, items))
|
답
kotlin code: 재귀를 사용하는 방법(timeout 발생)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| fun main() {
val (numOfItems, maxWeight) = readln().split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val items = Array(numOfItems) { readln().split(" ").let { Item(it.first().toInt(), it.last().toInt()) } }
println(p(numOfItems, maxWeight, items))
}
data class Item(val w: Int, val v: Int)
private fun p(n: Int, w: Int, items: Array<Item>): Int = when {
n == 0 || w == 0 -> 0
items[n-1].w <= w -> kotlin.math.max(p(n-1, w-items[n-1].w, items) + items[n-1].v, p(n-1, w, items))
else -> p(n-1, w, items)
}
|
kotlin code: 반복문을 사용하는 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| fun main() {
val (numOfItems, maxWeight) = readln().split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val items = Array(numOfItems) { readln().split(" ").let { Item(it.first().toInt(), it.last().toInt()) } }
println(p(numOfItems, maxWeight, items))
}
data class Item(val w: Int, val v: Int)
private fun p(numOfItems: Int, maxWeight: Int, items: Array<Item>): Int {
val p = Array(numOfItems + 1) { IntArray(maxWeight + 1) { 0 } }
for (n in (1..numOfItems)) {
for (w in (1..maxWeight)) {
val item = items[n - 1]
p[n][w] = if (w >= item.w) max(p[n - 1][w - item.w] + item.v, p[n - 1][w]) else p[n - 1][w]
}
}
return p.last().last()
}
|
Reference
Attachments
![식]() $\newline n:\;담을\,수\,있는\,물건의\,수(담을\,수\,있는\,물건의\,번호:\,0 \leq i \leq n-1)$
$\newline n:\;담을\,수\,있는\,물건의\,수(담을\,수\,있는\,물건의\,번호:\,0 \leq i \leq n-1)$![Dynamic Programming]()