백준 - 7576 토마토 풀이
문제
7576 토마토
풀이
1. 알고 있어야 할 점
- 하루가 지나면, 익은 토마토들의 인접한 곳에 있는 익지 않은 토마토들은 익은 토마토의 영향을 받아 익게 된다.
- 인접한 곳은 왼쪽, 오른쪽, 앞, 뒤 네 방향에 있는 토마토를 의미한다.
- 정수 1은 익은 토마토, 정수 0은 익지 않은 토마토, 정수 -1은 토마토가 들어있지 않은 칸을 나타낸다.(입력)
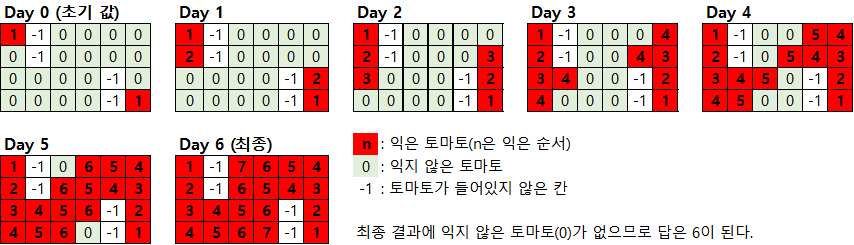
- 문제의 예제 1의 연산 과정
2. Step by Step
1. 입력을 2차원 배열에 저장한다.
- code
1
fun readInput(inputY: Int) = Array(inputY) {readln().split(" ").map{ it.toInt() }.toIntArray() }
2. 익은 토마토(1)의 좌표를 큐에 입력한다.
- code
1
fun initQueue(box: Array<IntArray>): java.util.Queue<Pair<Int, Int>> = java.util.LinkedList<Pair<Int, Int>>().apply {box.forEachIndexed { y, row -> row.forEachIndexed { x, column -> if (column == 1) this.offer(Pair(x, y)) } } }
3. 큐에서 값을 꺼낸다.(dequeue, poll)
4. 인접한 곳(왼쪽, 오른쪽, 앞, 뒤 네 방향)의 익지 않은 토마토(0)가 있는지 확인 한다.
5. 익지 않은 토마토의 좌표를 큐에 입력(enqueue, poll)한다.
6. 익지 않은 토마토의 좌표에 큐에 꺼낸 좌표의 값에 + 1한 값을 입력한다.
- ex) 큐에서 꺼낸 좌표의 토마토가 1이라면 2를 입력하고, 2라면 3을 입력한다.
- code (3 ~ 6)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
private fun search(inputX: Int, inputY: Int, box: Array<IntArray>, queue: java.util.Queue<Pair<Int, Int>>) { val (x, y) = queue.poll() if (x < inputX - 1 && box[y][x + 1] == 0) { queue.offer(Pair(x + 1, y)) box[y][x + 1] = box[y][x] + 1 } if (x > 0 && box[y][x - 1] == 0) { queue.offer(Pair(x - 1, y)) box[y][x - 1] = box[y][x] + 1 } if (y < inputY - 1 && box[y + 1][x] == 0) { queue.offer(Pair(x, y + 1)) box[y + 1][x] = box[y][x] + 1 } if (y > 0 && box[y - 1][x] == 0) { queue.offer(Pair(x, y - 1)) box[y - 1][x] = box[y][x] + 1 } }
7. 3 ~ 6을 큐가 빌 때까지 반복한다.
- code
1 2 3 4 5
fun bfs(inputX: Int, inputY: Int, box: Array<IntArray>, queue: java.util.Queue<Pair<Int, Int>>) { while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { search(inputX, inputY, box, queue) } }
8. 배열에 0이 존재하면 -1을 출력하고, 그렇지 않다면 배열에 입력된 수 중 가장 큰 값의 -1을 구한다.
- code
1
fun printDays(box: Array<IntArray>): Int = if(0 in box) -1 else box.max() - 1
9. 8에서 구한 값을 출력한다.
- code
1
println(getDays(box))
답
kotlin code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
fun main() {
val (inputX, inputY) = readln().split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val box = readInput(inputY)
val queue = initQueue(box)
bfs(inputX, inputY, box, queue)
println(getDays(box))
}
private fun initQueue(box: Array<IntArray>): java.util.Queue<Pair<Int, Int>> = java.util.LinkedList<Pair<Int, Int>>().apply {box.forEachIndexed { y, row -> row.forEachIndexed { x, column -> if (column == 1) this.offer(Pair(x, y)) } } }
private fun readInput(inputY: Int) = Array(inputY) {readln().split(" ").map{ it.toInt() }.toIntArray() }
private fun bfs(inputX: Int, inputY: Int, box: Array<IntArray>, queue: java.util.Queue<Pair<Int, Int>>) {
while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
search(inputX, inputY, box, queue)
}
}
private fun search(inputX: Int, inputY: Int, box: Array<IntArray>, queue: java.util.Queue<Pair<Int, Int>>) {
val (x, y) = queue.poll()
if (x < inputX - 1 && box[y][x + 1] == 0) {
queue.offer(Pair(x + 1, y))
box[y][x + 1] = box[y][x] + 1
}
if (x > 0 && box[y][x - 1] == 0) {
queue.offer(Pair(x - 1, y))
box[y][x - 1] = box[y][x] + 1
}
if (y < inputY - 1 && box[y + 1][x] == 0) {
queue.offer(Pair(x, y + 1))
box[y + 1][x] = box[y][x] + 1
}
if (y > 0 && box[y - 1][x] == 0) {
queue.offer(Pair(x, y - 1))
box[y - 1][x] = box[y][x] + 1
}
}
private fun getDays(box: Array<IntArray>): Int = if(0 in box) -1 else box.max() - 1
private operator fun Array<IntArray>.contains(element: Int): Boolean {
this.forEach { if(element in it) return true }
return false
}
private fun Array<IntArray>.max(): Int {
var max = this.first().first()
this.forEach { max = kotlin.math.max(max, it.max()) }
return max
}
private fun IntArray.max() = this.maxOf { it }
Attachments
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.